In this post, we are going to see how to run the playbook locally on our Localhost on the control machine. How to run Ansible Playbook locally is one of the questions I used to have before I learnt it.
Let me tell you how to Run Ansible Playbook Locally with Examples.
In fact, There are many ways to run ansible playbooks locally. Let us see each one and how they work.
There are four ways to run ansible playbook locally and we have listed them all here.
Method1: Specify Localhost in your hosts directive of your playbook.
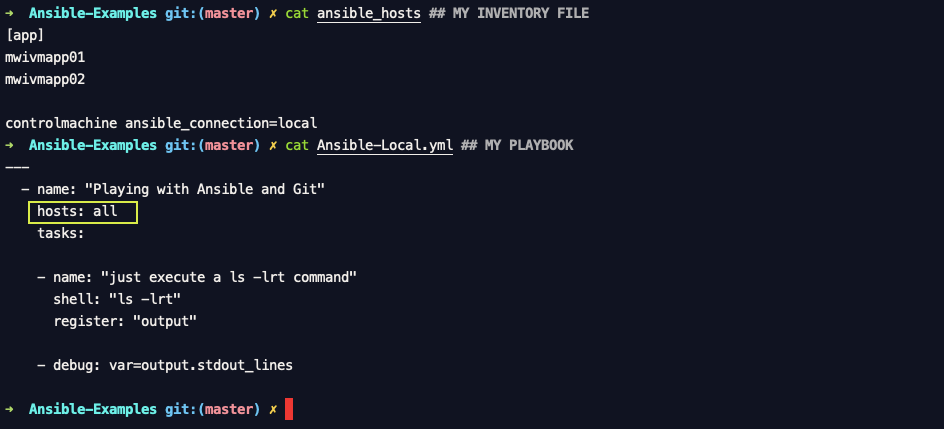
If you are running a playbook which you want to run on localhost (or) in other words you have a playbook you want to run locally. Within the playbook Just mention localhost in the hosts segment where you usually specify the host group. Consider the following playbook.
I have just specified the localhost in the hosts directive or key.
When you run this playbook. Despite you have no entry named localhost in your ansible inventory file /etc/ansible/hosts or custom hosts file specified with -i option. It would work
As an additional measure that it should run in localhost or locally. You can add a one more parameter named connection and set it to local
---
- name: "Playing with Ansible and Git"
hosts: localhost
connection: local
tasks:
- name: "just execute a ls -lrt command"
shell: "ls -lrt"
register: "output"
- debug: var=output.stdout_lines
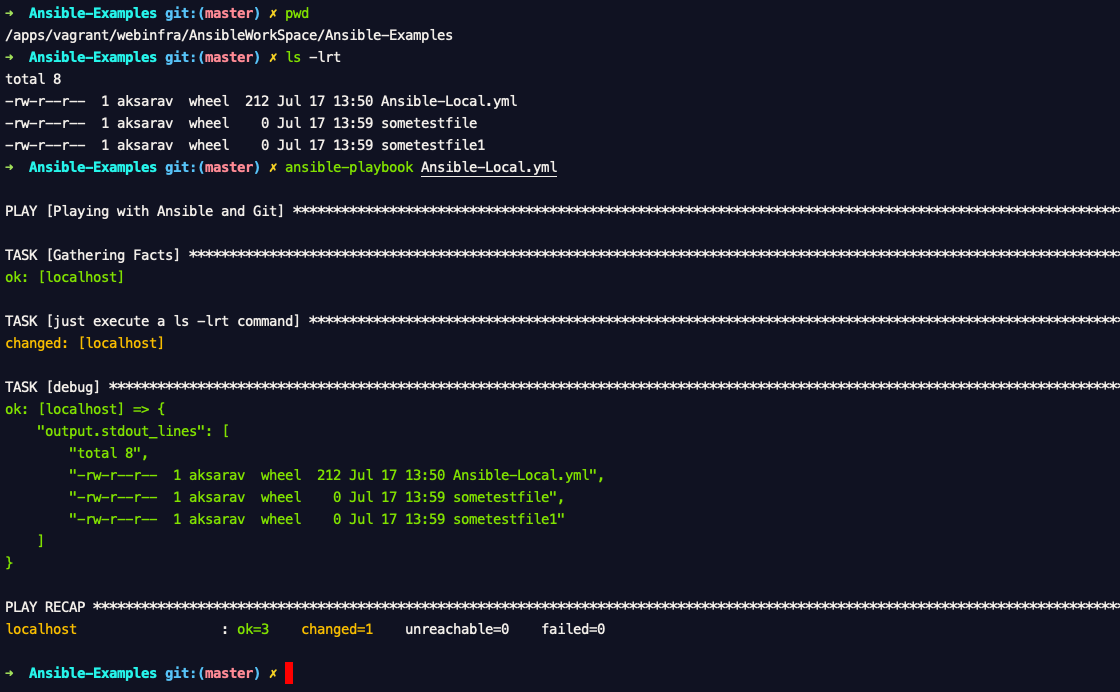
Here is the Test Results Snapshot of my Terminal.
Method2: Using local_action clause in the ansible playbook
This method is most recommended than the other 3 but it is always subjective to use it for your requirements.
Here is the example playbook that runs locally to create an EC2 instance connecting to AWS.
if you notice, we have not specified any hosts in here alternatively we have used local_action clause to specify that this task has to run local.
- name: create an ec2 instance
local_action:
module: ec2
image: ami-8caa1ce4
instance_type: m3.medium
key_name: mykey
group:
- web
- ssh
instance_tags:
type: web
env: production
here is the fully-functioning example of this method.
Method3: Add an entry in your Inventory
This is a second method to run ansible playbook locally.
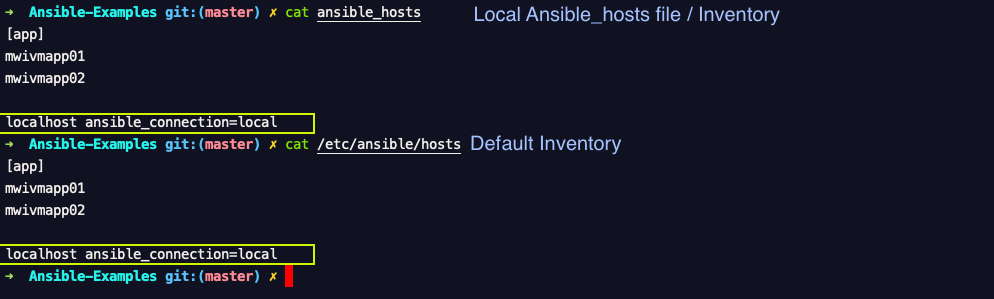
You can also explicitly define your localhost in your inventory file. your inventory file can be at the default location /etc/ansible/hosts or a customized ansible_hosts file in your present working directory.
Now if you run the same playbook we have given above you would yield the same results.
In the preceding Snapshot you can see the Yellow highlighted line were added to the inventory file specifying the localhost.
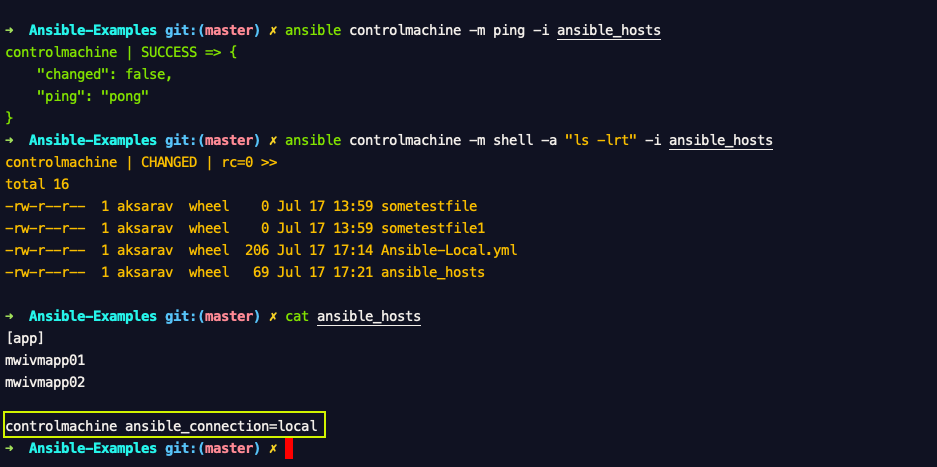
In this way if you would like to add your localhost with someother alias name. like "controlmachine" you can do the same.
Now you can refer your localhost by this name into your playbook like hosts: controlmachine
Method4: Specify in the Ansible Command line
This is a third method to run ansible playbook locally.
By Default, Ansible would run the playbook on the host group which is mentioned in the playbook with
But if you want to ignore all those hosts specified in the playbook and run it locally. You can use this method.
In this way. The hosts directive would be ignored and your task would run only on localhost.
I have a host group named app in my Ansible inventory file, it has two hosts beneath it and the playbook is defined to run on all the hosts in my inventory with hosts: all
When I run this playbook. the Playbook would be run against all the host groups specified in my inventory file.
For some reason, I don't want to run this playbook on any of remote hosts yet. I want to test it locally and run it locally. What should I do?
All you should do is this
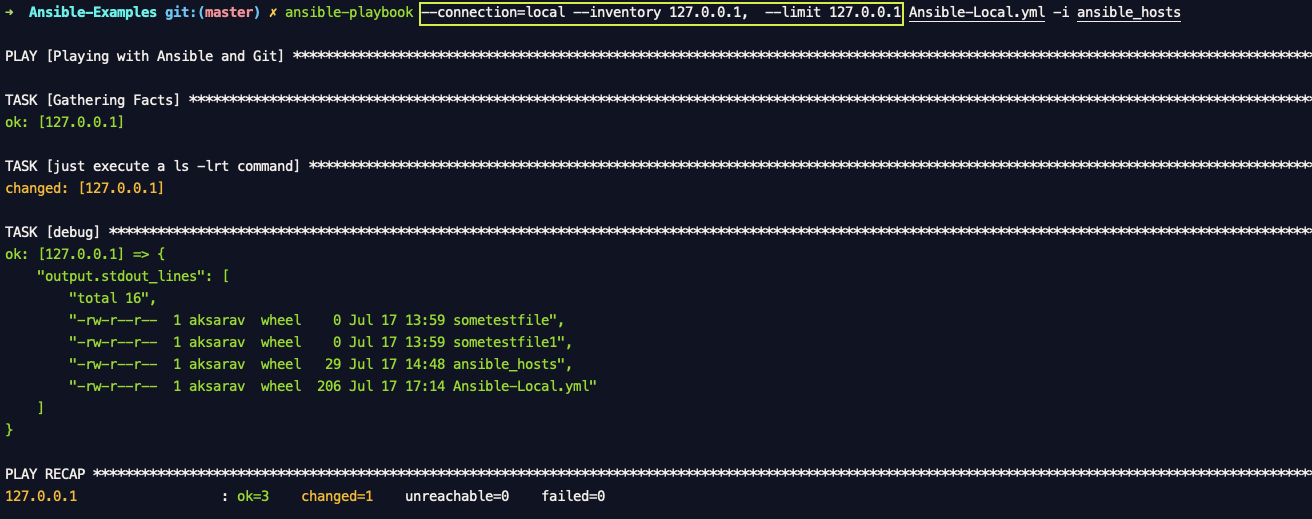
ansible-playbook \ --connection=local \ --inventory 127.0.0.1, \ --limit 127.0.0.1 Ansible-Local.yml -i ansible_hosts
Here
--connection - tells ansible to run the file locally.
– inventory - tells ansible to consider this host name as an inventory [ Comma at the end is IMPORTANT]
– limit - Limiting to only this host.
Why --limit is important here in method3
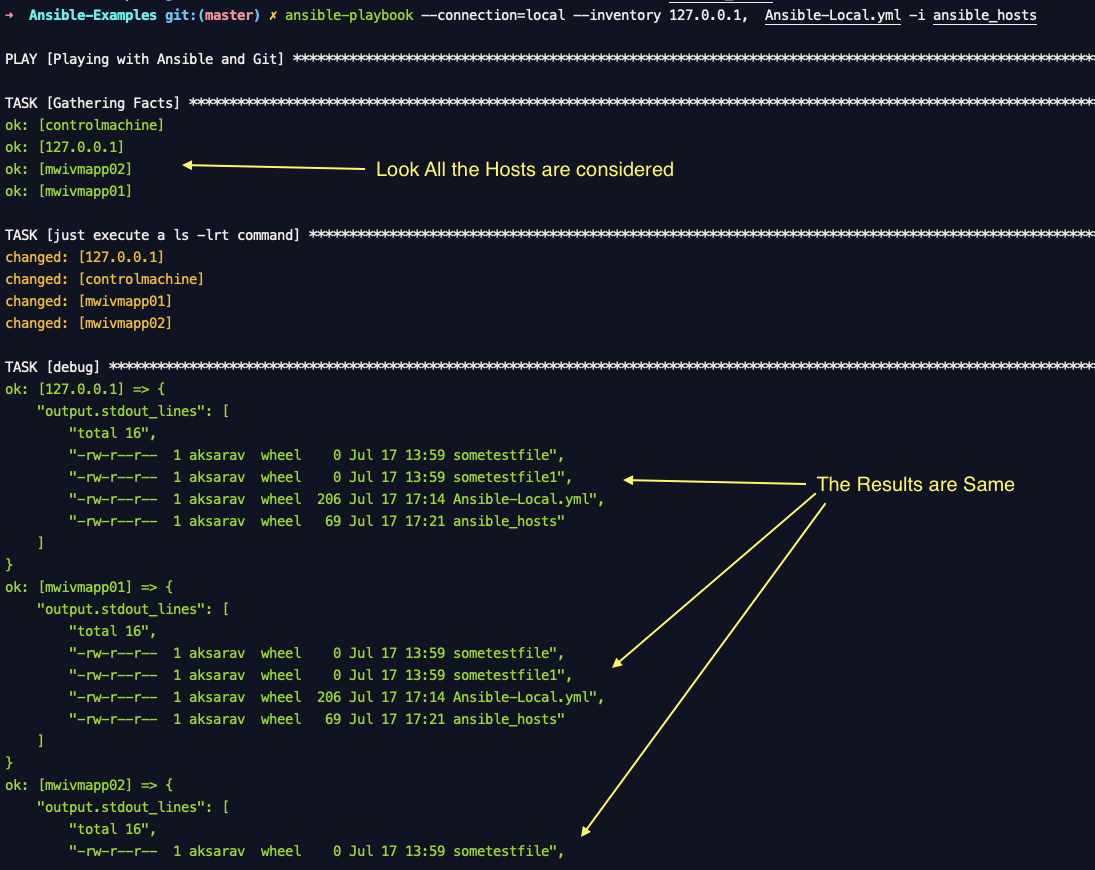
Note*: The Same command can be used without --limit but it would consider all the hosts mentioned in the hosts directive of the playbook.
Though it considers the remote servers it would not be able to run any task on those remote servers as we have set the conneciton to local.
Here is the confusing part.
What would ansible do here is that. It would execute the command locally but it will print the results in the name of remote servers.
Thanks,
Sarav AK

Follow me on Linkedin My Profile Follow DevopsJunction onFacebook orTwitter For more practical videos and tutorials. Subscribe to our channel
Signup for Exclusive "Subscriber-only" Content