In this post, we are going to see the Steps to create a Docker Image and Deploy to Kubernetes in 8 easy steps. This post is about the title of this post which is "How to Deploy docker image to kubernetes"
For this post, we have used minikube cluster and taken a Mac Desktop. Minikube can be installed in your Home PC and you can try all these steps as you are reading it.
Steps to Deploy Docker Image to Kubernetes.
- Creating a Dockerfile
- Building an Image from Dockerfile
- Validate if the Image is created and Listed
- Optionally upload to docker Hub to share with the world
- Start the Container from Image
- Create Manifest file for kubernetes
- Build and Create a POD from Manifest file
- Validate and Monitor the POD creation
- Check the newly created POD in Kubernetes DashBoard
Step1: Creating Dockerfile
Creating of Dockerfile. The file is designed to run redis in-memory database in an alpine base OS
# Use existing docker image as a base FROM alpine # Download and install dependency RUN apk add – update redis # EXPOSE the port to the Host OS EXPOSE 6379 # Tell the image what command it has to execute as it starts as a container CMD ["redis-server"]
Step2: Build an Image from Dockerfile
Build the Image using the Dockerfile we have developed
aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/docker/redisserver$ docker build -t saravak/redis . Sending build context to Docker daemon 2.048kB Step 1/4 : FROM alpine – -> 196d12cf6ab1 Step 2/4 : RUN apk add – update redis – -> Using cache – -> a1426a22089a Step 3/4 : EXPOSE 6379 – -> Using cache – -> 7c0fde02a01c Step 4/4 : CMD ["redis-server"] – -> Using cache – -> 8e1cc8b503d8 Successfully built 8e1cc8b503d8 Successfully tagged saravak/redis:latest aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/docker/redisserver$
Step3: Validate the image is created in docker images
Make sure the image is ready and listing in the docker images list
aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/docker/redisserver$ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE saravak/redis latest 8e1cc8b503d8 9 hours ago 6.9MB redis latest 0a153379a539 45 hours ago 83.4MB busybox latest 59788edf1f3e 46 hours ago 1.15MB tomcat latest 41a54fe1f79d 3 weeks ago 463MB alpine latest 196d12cf6ab1 3 weeks ago 4.41MB
Step4: Upload to hub.docker.com
Upload the image to the hub.docker.com repository for global access
aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/docker/redisserver$ docker login Login with your Docker ID to push and pull images from Docker Hub. If you don't have a Docker ID, head over to https://hub.docker.com to create one. Username: saravak Password: Login Succeeded aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/docker/redisserver$ docker push saravak/redis The push refers to repository [docker.io/saravak/redis] a63649d27e03: Layer already exists df64d3292fd6: Layer already exists latest: digest: sha256:dc0631a78737b5f0be09ad4c27b0120c916feb06d9bd7ce1fd6890925f5dd42b size: 739 aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/docker/redisserver$
Step5: Start the container from image
Start the container using the Image we just built just to make sure that the image can be instantiated as a container with no issues.
aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/docker/redisserver$ docker container run -d -it – name rediscontainer saravak/redis:latest b9824eb84fd75fdf511149284db8fef4b1d03dce6be5e8527e38159b672f115c aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/docker/redisserver$ docker container list CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES b9824eb84fd7 saravak/redis:latest "redis-server" 27 seconds ago Up 25 seconds 6379/tcp rediscontainer
Note*: Till here you were Creating a Docker Image and working on Docker Command Line Interface.
As you are entering into the Kubernetes Phase. I would like to Present you two Different options to Create a Kubernetes Container from your Docker Image aka Dockerfile.
The Second method is a Quick one where you Do not have to write any Instructions like YAML/JSON files and let Kubernetes do the hard work for you,
On the other hand, The First Method is where you define all the configuration elements on what Kubernetes should do with your image
- Create Manifests and build things using Kubectl create command (Recommended)
- Deploy Docker Image to Kubernetes Quickly with - Kubectl run command ( Deprecated)
You make the choice.
Method1: Kubernetes Tasks with Manifest file
Step6: Create Manifest file for Kubernetes
Create a Manifest file to create a Simple and Straight forward POD [Without replica and Scaling]
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: redis-pod spec: containers: - name: redis-container01 image: saravak/redis:latest ports: - containerPort: 6379
Step7: Build and Create POD from Manifest file
Create a POD using Kubectl command using the Manifest file we have created in Step6
aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/kubernetes$ kubectl create -f create-redispod.yml pod/redis-pod created
Step8: Validate the pod creation and find more information
Get the status and more detailed information on the newly created POD
aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/kubernetes$ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE hello-minikube-7c77b68cff-pd4x2 1/1 Running 1 11h redis-pod 1/1 Running 0 2m aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/kubernetes$ kubectl get pods/redis-pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE redis-pod 1/1 Running 0 2m aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/kubernetes$ kubectl describe pods/redis-pod Name: redis-pod Namespace: default Node: minikube/192.168.64.2 Start Time: Thu, 04 Oct 2018 21:58:28 +0530 Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Status: Running IP: 172.17.0.6 Containers: redis-container01: Container ID: docker://c7bc7ce68272493477249da617ea042ca5191b6b7b4ef89f9490dab8584e0fb4 Image: saravak/redis:latest Image ID: docker-pullable://saravak/redis@sha256:dc0631a78737b5f0be09ad4c27b0120c916feb06d9bd7ce1fd6890925f5dd42b Port: 6379/TCP Host Port: 0/TCP State: Running Started: Thu, 04 Oct 2018 21:58:36 +0530 Ready: True Restart Count: 0 Environment: <none> Mounts: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-t5c7w (ro) Conditions: Type Status Initialized True Ready True PodScheduled True Volumes: default-token-t5c7w: Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret) SecretName: default-token-t5c7w Optional: false QoS Class: BestEffort Node-Selectors: <none> Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s Events: Type Reason Age From Message – – – -- – – – – – – ----- Normal Scheduled 2m27s default-scheduler Successfully assigned redis-pod to minikube Normal SuccessfulMountVolume 2m27s kubelet, minikube MountVolume.SetUp succeeded for volume "default-token-t5c7w" Normal Pulling 2m26s kubelet, minikube pulling image "saravak/redis:latest" Normal Pulled 2m20s kubelet, minikube Successfully pulled image "saravak/redis:latest" Normal Created 2m19s kubelet, minikube Created container Normal Started 2m19s kubelet, minikube Started container aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/kubernetes$
Method2: Quick Deployment of Docker Image with No Manifest
Step6: Create a Pod from Docker Image
In this step, we are instantiating our Docker Image as Container.
As you know the basic and the core element of Kubernetes is POD and that's a logical group of one or more containers. A Container cannot run standalone in Kubernetes it must always run inside a POD.
So Creating a POD is technically creating a Container
$ kubectl run redis-pod – image=saravak/redis – port=6379 – generator=run/v1
kubectl run – generator=run/v1 is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl create instead.
replicationcontroller/redis-pod created
If you look at the preceding snippet closely,
It creates a replication Controller in place of POD. But do not worry, Replication Controller is there to efficiently manage and scale the POD and it is a layer above the POD.
Now Let us validate if our POD is ready and created.
What is Replication Controller - A Short note
A ReplicationController is a Kubernetes resource that ensures its pods are always kept running. If the pod disappears for any reason, such as in the event of a node disappearing from the cluster or because the pod was evicted from the node, the replication controller notices the missing pod and creates a replacement pod.
Step7: Make Sure the POD is created and Ready.
Using Kubectl get command, Make Sure the POD is created.
Since the Replication Controller is in place and it managed the POD, the POD name would be dynamic
$ kubectl get pods|egrep -i "^NAME|redis-pod"
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
redis-pod-jsrvz 1/1 Running 0 19m
Step8: Validate the pod creation and find more information
Get the status and more detailed information on the newly created POD
aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/kubernetes$ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE hello-minikube-7c77b68cff-pd4x2 1/1 Running 1 11h redis-pod-jsrvz 1/1 Running 0 2m aksarav@middlewareinventory:/apps/kubernetes$ kubectl get pods/redis-pod-jsrvz NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE redis-pod 1/1 Running 0 2m
$ kubectl describe pods/redis-pod-jsrvz
Name: redis-pod-jsrvz
Namespace: default
Node: minikube/10.0.2.15
Start Time: Sat, 04 May 2019 19:29:43 +0530
Labels: run=redis-pod
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 172.17.0.10
Controlled By: ReplicationController/redis-pod
Containers:
redis-pod:
Container ID: docker://13d54838011e655ac392065d60da0706f0bf27f4e3b6df11d7a013879a6d52e4
Image: saravak/redis
Image ID: docker-pullable://saravak/redis@sha256:dc0631a78737b5f0be09ad4c27b0120c916feb06d9bd7ce1fd6890925f5dd42b
Port: 6379/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Sat, 04 May 2019 20:31:22 +0530
Last State: Terminated
Reason: Completed
Exit Code: 0
Started: Sat, 04 May 2019 19:29:54 +0530
Finished: Sat, 04 May 2019 20:23:46 +0530
Ready: True
Restart Count: 1
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-2fg4d (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-2fg4d:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-2fg4d
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
– – – -- – – – – – – -----
Normal Scheduled 66m default-scheduler Successfully assigned redis-pod-jsrvz to minikube
Normal SuccessfulMountVolume 66m kubelet, minikube MountVolume.SetUp succeeded for volume "default-token-2fg4d"
Normal Pulling 66m kubelet, minikube pulling image "saravak/redis"
Normal Pulled 66m kubelet, minikube Successfully pulled image "saravak/redis"
Normal Created 66m kubelet, minikube Created container
Normal Started 66m kubelet, minikube Started container
Normal SuccessfulMountVolume 5m31s kubelet, minikube MountVolume.SetUp succeeded for volume "default-token-2fg4d"
Normal SandboxChanged 5m31s kubelet, minikube Pod sandbox changed, it will be killed and re-created.
Normal Pulling 5m30s kubelet, minikube pulling image "saravak/redis"
Normal Pulled 5m6s kubelet, minikube Successfully pulled image "saravak/redis"
Normal Created 5m6s kubelet, minikube Created container
Normal Started 5m6s kubelet, minikube Started container
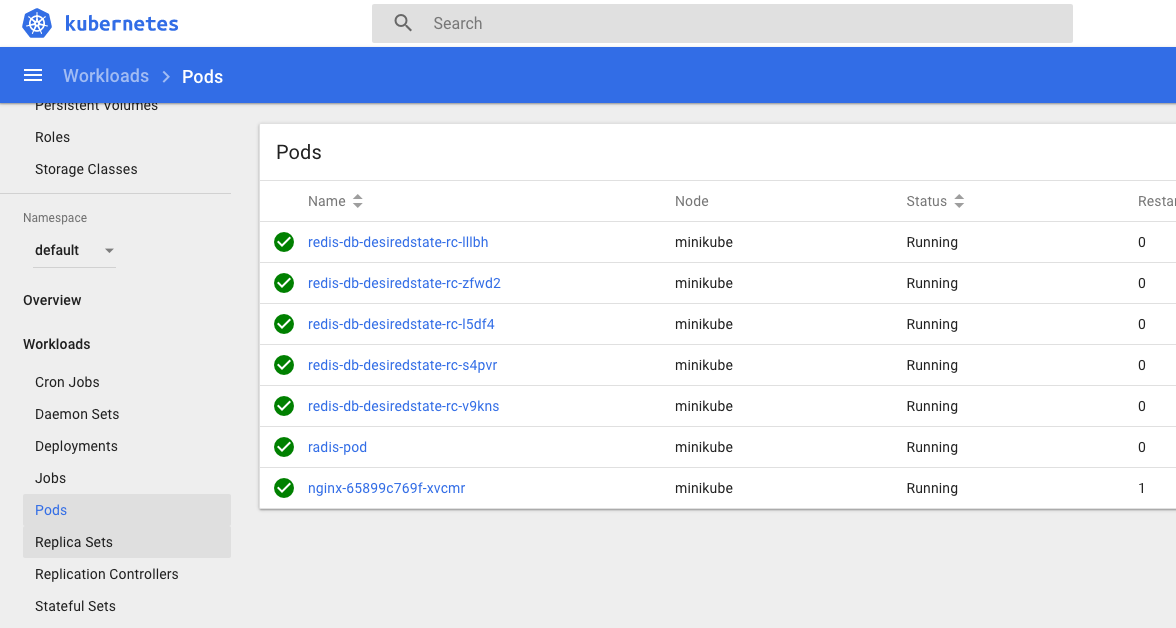
Validation: check the newly created pod in Kubernetes Dashboard (GUI) - minikube
run the following command and It will open the dashboard in your default browser
minikube dashboard
Under NameSpace - Default -> Workloads -> pods
Make Sure that your POD is present.
That'a all this is how we can deploy a Docker image to Kubernetes in Eight Simple Steps.
Hope this helps.
Thanks,
SaravAK

Follow me on Linkedin My Profile Follow DevopsJunction onFacebook orTwitter For more practical videos and tutorials. Subscribe to our channel
Signup for Exclusive "Subscriber-only" Content