The Objective
The purpose of this post is to explain with an example of how ansible initiate the reboot and wait for the reboot to complete
There are cases where we want our remote nodes to be rebooted or restarted. For example, Take the Patching as an example. As part of quarterly patching, we upgrade the installed software and packages and do various other stuff along with a final reboot to make the changes effective.
When we reboot the server(box). you might get your ansible play failed with the error “Shared connection closed”
But this can be avoided and you can reboot the box and wait for the server to come back up and execute the post-reboot validations or checks.
How to reboot and wait for it to complete with ansible
There are many methods to accomplish this
For Ansible 2.7 and more – There is a dedicated reboot module
For previous versions – Either use wait_for or wait_for_connection
Since the reboot module of Ansible 2.7 is very simple and efficient and also considering that most people is still behind ansible 2.7. In this post, we are going to see wait_for and wait_for_connection modules of ansible to get our task accomplished
Consider the following playbook I have created for linux patching. It performs yum update and reboot the box and print the uptime
The Ansible Playbook with wait_for module
---
- name: Patch the server and Reboot
hosts: app
tasks:
- name: Patch the server
become: yes
become_user: root
tags: Patch
shell: "yum -y update"
register: patchresult
- name: Reboot the server
tags: reboot
become: yes
become_user: root
shell: "sleep 5 && reboot"
async: 1
poll: 0
- name: Wait for the reboot and reconnect
wait_for:
port: 22
host: '{{ (ansible_ssh_host|default(ansible_host))|default(inventory_hostname) }}'
search_regex: OpenSSH
delay: 10
timeout: 60
connection: local
- name: Check the Uptime of the servers
shell: "uptime"
register: Uptime
- debug: var=Uptime
Explanation
In the preceding playbook, we have four tasks.
The first task is running a single command “yum -y update” over the shell module, which is responsible for updating the packages and software in the boxes.
The Second task is to reboot the server. we execute the reboot command over shell module. The task contains two important arguments which are async and poll
If you try to take the sleep command away from the shell module and just keep the reboot command. The Playbook will get terminated with the connection closed exception.
The Sleep command followed by reboot on success using && symbols are strategically placed to give ansible a little time to get it all together. If you simply execute reboot or shutdown -now commands the ansible connection will be dropped.
So some Sleep is always good.
That's also the reason we cannot use command module Over shell, cause the command module does not support logical and - &&
async: By default, the tasks in playbook block the execution till it gets completed. If you mention async in the task. It will be run asynchronously, in other words, it runs detached and in the background. ansible master keeps track of this task by using the poll interval. it accepts the time in seconds it should keep the connection open before times out
poll: Time in seconds, at what interval the ansible master should poll the Job/task to know whether it is completed.
when the poll is set to 0 seconds, Ansible will fire the task and forget it. which is used specifically in here so that despite the remote servers shutdown the playbook will still be on
The Third task is wait_for. which is our primary focus so let me explain all the arguments of this task
port: we are waiting for the port 22 (SSH Default port) to be open
host: we are using the ansible built-in variables here inventory_hostname or ansible_host which will represent the current host from of the host group defined in the playbook (app)
search_regex: we are looking for a word OpenSSH once the Port is open.
delay: Delay in seconds before starting the validation
timeout: timeout the execution after defined seconds.
connection: Execute the connection from local (master)
When the connection is set to local. The Master will try to connect to the remote boxes from the master. It is more like executing nc or telnet command to make sure the port is open
The Ansible playbook with Wait_for_connection module
---
- name: Patch the server and Reboot
hosts: app
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Patch the server
become: yes
become_user: root
tags: Patch
shell: "yum -y update"
register: patchresult
- name: Reboot the server
tags: reboot
become: yes
become_user: root
shell: "sleep 5 && reboot"
async: 1
poll: 0
- name: Wait for the reboot to complete if there was a change.
wait_for_connection:
connect_timeout: 10
sleep: 5
delay: 5
timeout: 300
- name: Check the Uptime of the servers
shell: "uptime"
register: Uptime
- debug: var=Uptime
Explanation
connect_timeout : Maximum number of seconds to wait for a connection to happen before closing and retrying.
delay : Number of seconds to wait before starting to poll.
sleep : Number of seconds to sleep between checks.
timeout : Maximum number of seconds to wait for.
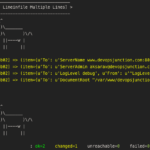
The Execution Results
Since, Ansible 2.7. You can just do the reboot effortlessly and wait for the server to come back up using reboot module.
Hope it helps.
Thanks,
Sarav AK

Follow me on Linkedin My Profile Follow DevopsJunction onFacebook orTwitter For more practical videos and tutorials. Subscribe to our channel
Signup for Exclusive "Subscriber-only" Content