AWS CLI is a very great help when it comes to efficiently managing your AWS Cloud Infrastructure and your EC2 instances.
While we are managing our AWS Infrastructure, we cannot always afford to login to the AWS console all the time and it is not recommended from the security perspective as well.
So the key here is the Programmatic Access with AWS CLI.
This is what we are going to do in this post.
- Setup your Programmatic Access - Create Access Key and Key Secret.
- Install AWS CLI
- Configure AWS CLI
- Execute the AWS CLI Command line examples to List EC2 instances command line.
Let us perform these aforementioned steps one by one.
Setup your Programmatic Access - Create Access Key
If you would like to create a new user in IAM along with the Access Key follow these steps.
-
Login to AWS Console
-
In the services go to IAM
-
Create a User and Click on map existing Policies
-
Choose UserName and Select the Policy (Administrator Access Policy)
-
Create user
-
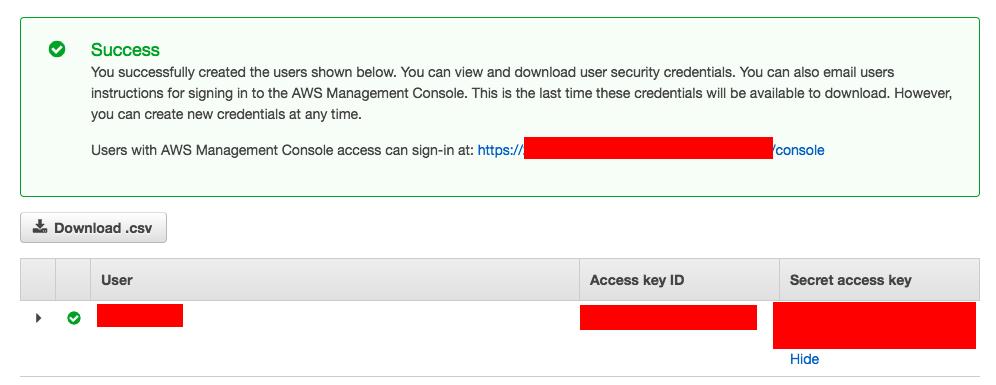
Final Stage would present the AccessKEY and Secret Access like given below.
If you would like to Choose the existing user and create an Access Key follow this
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the IAM console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/.
- In the navigation pane, choose Users.
- Choose the name of the user whose access keys you want to create, and then choose the Security credentials tab.
- In the Access keys section, choose to Create an access key.
- To view the new access key pair, choose Show. You will not have access to the secret access key again after this dialog box closes. ( Refer the image given above)
Install AWS CLI
Based on your base machine the AWS CLI installation and command might vary.
Amazon has given a clear instructions on how to install AWS CLI on each platform. Choose any of the following links and get your AWS CLI installed and ready
- Installing AWS CLI version 2 on Linux or Unix
- Installing AWS CLI version 2 on macOS
- Installing AWS CLI version 2 on Windows
Configure AWS CLI
I presume that you have installed the AWS CLI package and if everything went well.
You should be able to see the version of the AWS CLI installed when entering the following command in your terminal or command prompt
aws – version
I am using the AWS CLI Version1 as CLI Version 2 is still on Beta.
Now it is a time to configure the AWS CLI, Just enter the following command and you would be prompted a few questions about the Access Key and Passwords.
aws configure
it would look like this as you are setting it up.
You enter your own AWS Access Key ID and Secret Access Key and the one is given below is not correct. Just a made up.
➜ ~ aws configure AWS Access Key ID [None]: AKIAS790KQGK63WUK6T5 AWS Secret Access Key [None]: kkQEiBjJSKrDkWBLO9G/JJKQWIOKL/CpHjMGyoiJWW Default region name [None]: us-east-1 Default output format [None]:
Well done. You are ready with AWS CLI
Quick Syntax of AWS CLI Commands
Before we are going in further, let me quickly give you the syntax of AWS CLI commands
aws [options] <command> <subcommand> [<subcommand> ...] [parameters]
aws CLI should be invoked with command and a subcommand. AWS CLI provides us huge list of commands and their associated sub commands and their documentation is also awesome.
It would take years for someone to write about all these commands and our objective is very specific and we are going to take one Single command named describe-instances
So let us move on and explore what it has got for us!!. We have given 7 examples of AWS CLI EC2 in this post.
AWS CLI EC2 Examples - Describe instances
- List All instances in your AWS infra (Single Region)
- List only Running instances
- Get a Specific list of Fileds using Query Parameter
- List Ec2 instance by tag value
- Describe a Specific instance using the instance ID
- List instances by Instance Type
- List instances by Availability Zone
- List the instances mapped to the Security Group.
- List the running instances with PrivateIP, PublicIP and VPC ID
- List All the instances in all regions - Run Any AWS Command in all regions
- List SPOT instances using aws cli EC2
- List OnDemand Instances using aws cli EC2
- List EC2 Instances with IAM and Security Group
Example1: List All Instances in your AWS infrastructure from Default Region
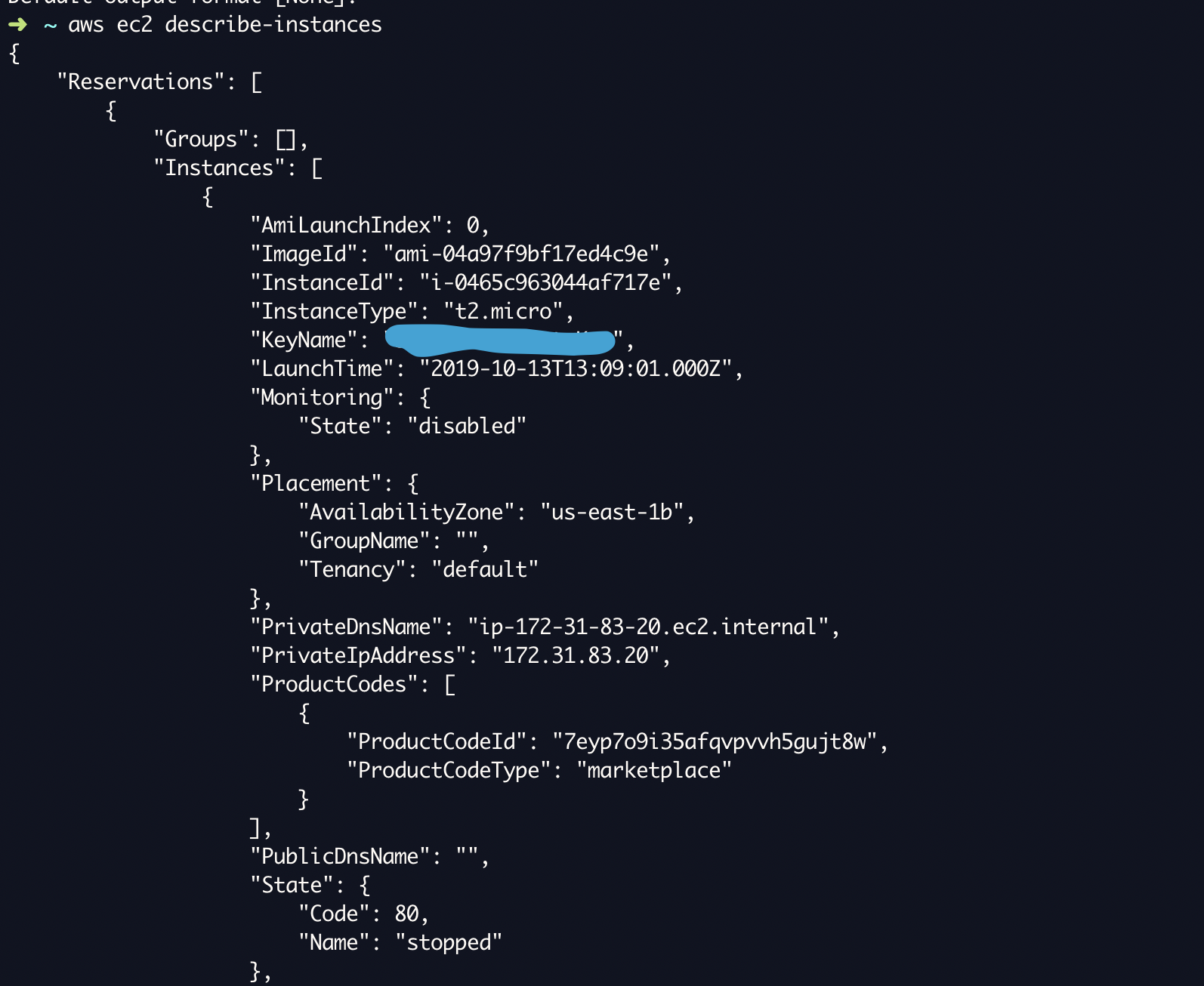
If everything was done right. When you are running the following command you would see a Nicely formatted JSON output something just like this.
This command would list all the instances from your default region defined by you.
The command is
aws ec2 describe-instances
It would fetch all the data from your aws account and display the results as JSON format. but this is NOT a human-readable format.
So ansible AWS CLI has great filters for you in place to help.
If you would like to describe the instances in JSON from other regions you can specify the region name on the command
aws ec2 describe-instances – region us-east-2
Example2: List only Running instances as a Table using AWS CLI EC2
Here is the command we are going to execute. It is a bit complex to the previous command we have used. But it can be easily understood.
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" \
--filters Name=instance-state-name,
Values=running \
--output table
So we are using three main parameters/flags here with aws ec2 describe-instances command.
--query accepts the JSON query, To limit the fields returned or to customize the list of fields on the result
--filters accepts a list of filters, A Search String alike. to get the list of filters refer here
--output to customize the format of the output, JSON (or) TABLE
With the help of the --query field we are displaying only the Name, PublicIP, Status fields from the entire data. We can customize it further by choosing more or less fields using the query.
Consider the following example.
Example3: Getting More Fields using the Query Parameter. Get the Machine type
Here is the command we are going to use to get the list of running instances with Name, PublicIP, Status along with machine type
ansible aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,Type:InstanceType,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=tag:Name,Values='*'" \
--output table
Example4: Get the servers based on a String availability on the tag using AWS CLI EC2
While we are creating the servers, we give meaningful tags to the server Name is one famous tag name we are giving for all the ec2 instances we are creating.
Often we would give some useful information on this such as Hostname, Application Name, Environment Name etc.
Let's suppose that this Name the field is having the environment names such as dev, prod, uat on all the servers present in your aws infrastructure
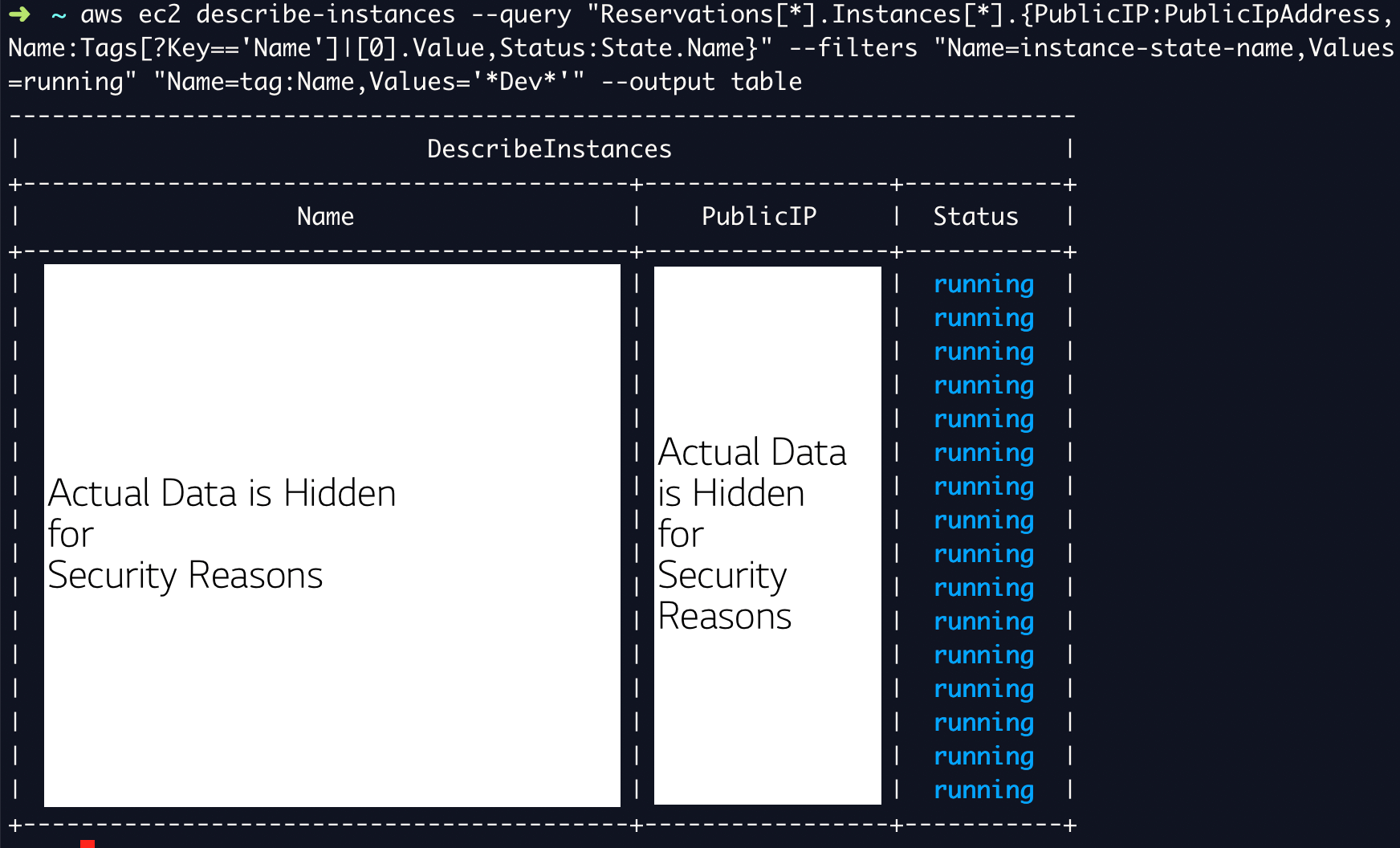
To list only the Dev servers. the following command would help
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running"
"Name=tag:Name,Values='*Dev*'" \
--output table
Look at the highlighted part on the preceding snippet and you would understand that we are using the Search string *Dev* to get only the Development servers.
We are also specifying the tag name in which the search has to happen with Name=tag:Name
Example5: Describe a Specific instance by Instance ID using AWS CLI EC2
Sometimes all you want to know is a configuration of a Single instance and if you have the instance-id with you. you can do it easily with aws ec2 describe-instances command line.
Here is the command,
The --instance-ids parameter can accept one or more instance ids. The output will be printed as JSON unless modified with --query and --output
aws ec2 describe-instances – instance-ids i-1234567890abcdef0
Example6: List all running instances based on the Instance Type. t2.medium, t2.large etc.
List only large instances in a running state
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,Type:InstanceType,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=instance-type,Values='*large*'" \
--output table
List only medium and micro instances
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,Type:InstanceType,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=instance-type,Values='t2.medium','t2.micro'" \
--output table
You can get the output as JSON as well, Not just Table
I know you might think that all the examples are having
--outputformat as table. Based on your requirement you can use eithertableortextorjsonwith thisoutputparameter.here is the example.
aws ec2 describe-instances \ --query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,Type:InstanceType,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" \ --filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=instance-type,Values='t2.medium','t2.micro'" \ --output json
Example7: List instances based on the Availability Zone using AWS CLI EC2
You can also list the instances based on their availability zone
here is the command
aws ec2 describe-instances \
– filters Name=availability-zone,Values=us-east-2c
Example 8: List the instances associated with a Specific Security Group
I think, we often get a requirement to check how many instances are using a particular security group and here is the aws ec2 command to get that done for us
Here my security group name is Application-Server and here is the command I would use to get the list of EC2 instance associated with the Security group
Here I am using the instance.group-name filter to get that done.
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,Type:InstanceType,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=instance-type,Values='t2.medium','t2.micro'" "Name=instance.group-name,Values='Application-Server'" \
--output table
As it does not print the Security Group data in the table format. If you want to reverify. You can use the following command which lists the Security-Groups associated with the EC2 instance. Just to cross verify.
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,Type:InstanceType,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name,SecurityGroups:SecurityGroups[*]}" \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=instance-type,Values='t2.medium','t2.micro'" "Name=instance.group-name,Values=Application-Server" \
--output json
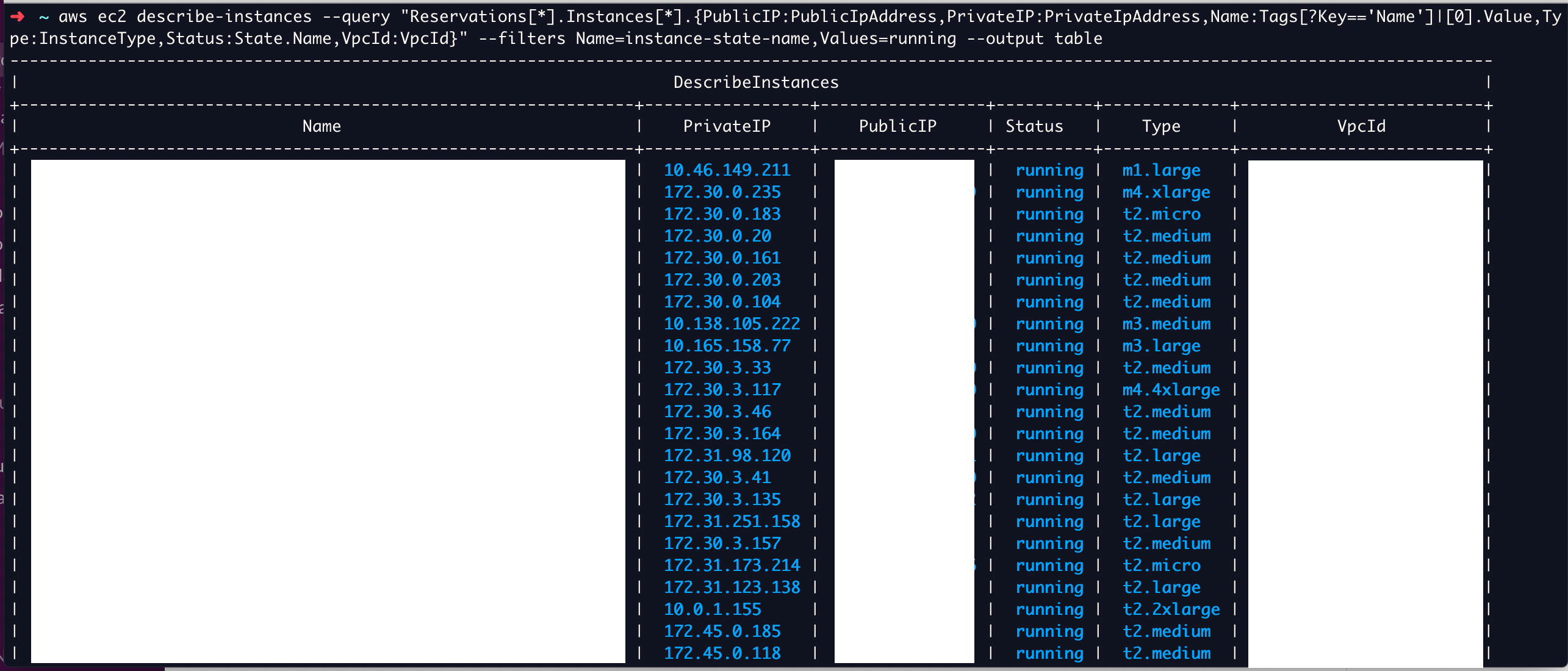
Example 9: List the running instances with PrivateIP, PublicIP and VPC ID
In this example, we are going to see how to use AWS CLI EC2 to list the running instances with more details like InstanceType, PrivateIP, PublicIP and VPC ID etc
aws ec2 describe-instances
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,PrivateIP:PrivateIpAddress,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Type:InstanceType,Status:State.Name,VpcId:VpcId}"
--filters Name=instance-state-name,Values=running
--output table
Here is the execution output of this command looks like
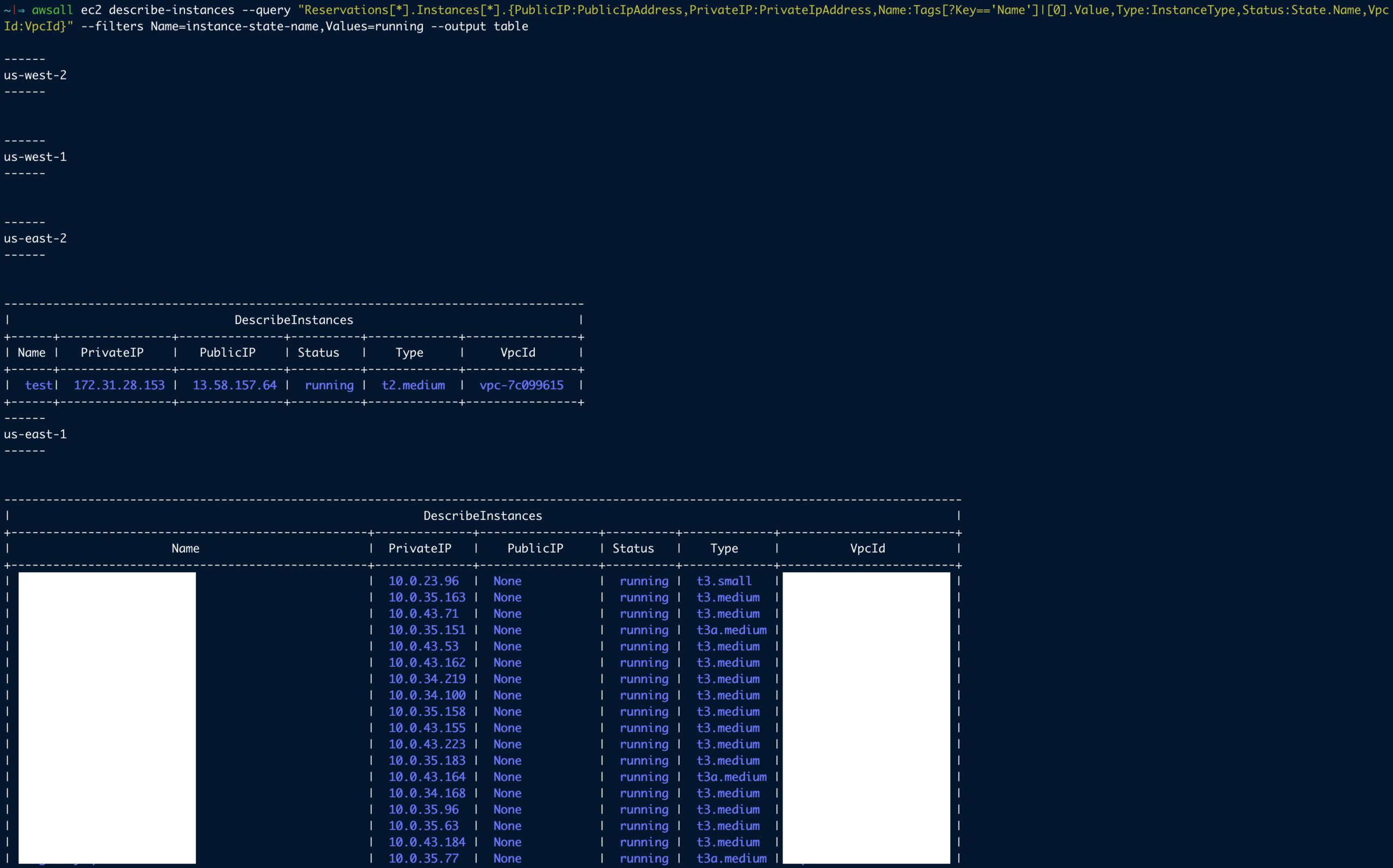
Example 10: List All the instances in all regions
By default AWS CLI would be picking up your default region while executing the command. What if you want to List All the instances in all regions.
we have a solution for it. Refer the following post where we talk about our new tool awsall
Run AWS CLI commands on All regions - awsall | Devops Junction
You can execute all the aws commands with awsall with modification.
For example, Take the example 9 and replace the awswith awsall and execute it.
awsall ec2 describe-instances – query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,PrivateIP:PrivateIpAddress,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Type:InstanceType,Status:State.Name,VpcId:VpcId}" – filters Name=instance-state-name,Values=running – output table
It will be executed on all AWS regions and give you the result.
Example 11: List SPOT instances using aws CLI EC2
At times we want to list instances based on their billing life cycle, SPOT or On Demand.
Here is the aws CLI ec2 command to list. only spot instances
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PrivateIP:PrivateIpAddress,Type:InstanceType,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name,LifeCyle:InstanceLifecycle }" \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=instance-type,Values='*'" \
--output table | grep -i spot
This would print the details in the form of a table.
If you want the output as a CSV. you can use the following command. we have used awkcommand to format the output to CSV along with text output format.
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PrivateIP:PrivateIpAddress,Type:InstanceType,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name,LifeCyle:InstanceLifecycle }" \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=instance-type,Values='*'" \
--output text |grep -i spot | awk '{print $1","$2","$3","$4","$5}'
Example 12: List ON-Demand instances using aws CLI EC2
to list only the OnDemand EC2 instances on your AWS account. You can use the following command
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PrivateIP:PrivateIpAddress,Type:InstanceType,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name,LifeCyle:InstanceLifecycle }" \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=instance-type,Values='*'" \
--output table|grep -iv spot
as on-demand instances would not have any InstanceLifeCycle reference like SPOT. we are trying to list all instances without spot using grep -iv
If you want the output to be in CSV format you can use the below command
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PrivateIP:PrivateIpAddress,Type:InstanceType,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name,LifeCyle:InstanceLifecycle }" \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=instance-type,Values='*'" \
--output text|grep -iv spot|awk '{print $1","$2","$3","$4","$5}'
Example13: List EC2 instances with IAM and Security Group
In this example, we are listing the aws EC2 instances with their IAM security role and security group configuration.
Get all running instances with their IAM and security group using aws cli
aws ec2 describe-instances – query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,PrivateIP:PrivateIpAddress,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name'].Value|[0],Status:State.Name,VpcId:VpcId,InstanceID:InstanceId,Groups:join(',',NetworkInterfaces[].Groups[].GroupId),IamInstanceProfile:IamInstanceProfile.Arn}" – filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" – output json
Get all stopped instances with their IAM and security group using aws cli
aws ec2 describe-instances – query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,PrivateIP:PrivateIpAddress,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name'].Value|[0],Status:State.Name,VpcId:VpcId,InstanceID:InstanceId,Groups:join(',',NetworkInterfaces[].Groups[].GroupId),IamInstanceProfile:IamInstanceProfile.Arn}" – filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=stopped" – output json
Filter instances with a specific name. done using the filters
aws ec2 describe-instances – query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIP:PublicIpAddress,PrivateIP:PrivateIpAddress,Name:Tags[?Key=='Name'].Value|[0],Status:State.Name,VpcId:VpcId,InstanceID:InstanceId,Groups:join(',',NetworkInterfaces[].Groups[].GroupId),IamInstanceProfile:IamInstanceProfile.Arn}" – filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" "Name=tag:Name,Values=*EKS*" – output json
You can notice we are using *EKS* to filter Ec2 instances which have EKS on their name.
We are also using a special function of JMESPATH named join to flatten the array and convert all the elements to a single-line string with a comma
Since the IAM role would come as a full ARN and at times a single instance would have multiple security groups, displaying this data as a table using --output table may not be the right choice.
Conclusion
While there are so many modules still that are not covered in this post. I hope that this gives you a good start on the AWS CLI command line.
Feel free to ask any questions in the comments section
Cheers
Sarav AK

Follow me on Linkedin My Profile Follow DevopsJunction onFacebook orTwitter For more practical videos and tutorials. Subscribe to our channel
Signup for Exclusive "Subscriber-only" Content